| |
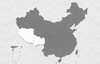
 The
People's Republic of China is divided into 23 provinces, five autonomous
regions, four municipalities directly under the Central Government,
and two special administrative regions. As one of the five autonomous
regions, the Tibet Autonomous Region is inhabited mainly by the Tibetan
race. The
People's Republic of China is divided into 23 provinces, five autonomous
regions, four municipalities directly under the Central Government,
and two special administrative regions. As one of the five autonomous
regions, the Tibet Autonomous Region is inhabited mainly by the Tibetan
race.
 The
Tibet Autonomous Region is situated in the southwestern border area
of the People's Republic of China, and the southwestern part of the
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Lying at 78°25'- 99°06'E and 26°44'-
36°32'N, it abuts the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in the
north, Qinghai Province in the northeast, Sichuan Province in the
east, and Yunnan Province in the southeast. It also has a 4,000 km
border with the neighboring countries of Myanmar, India, Bhutan and
Sikkim as well as Kashmir in the south and west. The
Tibet Autonomous Region is situated in the southwestern border area
of the People's Republic of China, and the southwestern part of the
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Lying at 78°25'- 99°06'E and 26°44'-
36°32'N, it abuts the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in the
north, Qinghai Province in the northeast, Sichuan Province in the
east, and Yunnan Province in the southeast. It also has a 4,000 km
border with the neighboring countries of Myanmar, India, Bhutan and
Sikkim as well as Kashmir in the south and west.
Topography
Known as the "roof of the world'', the Tibet Autonomous Region forms
the major part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Its varied topography
is composed of three different natural areas:
Northern Tibet Plateau: Lying among the
Kunlun, Tanggula, Kangdese and Nyainqentanglha mountains, the plateau
covers two-thirds of the autonomous region.
Southern Tibet Valley: Lying between the Kangdese
and Himalayan mountains, the valley is drained by the Yarlung Zangbo
River and its tributaries.
Eastern Tibet Canyon: The canyon is formed by some high mountains
extending east-west before turning south-north that belongs to the
Hengduan Mountain Range.
 The
Tibet Autonomous Region comprises six typographical types--extra-high
mountains, high mountains, medium-high mountains, low mountains, hills
and plains. The region also features glacier edge, karst, sandstorm
and volcanic topographies. The
Tibet Autonomous Region comprises six typographical types--extra-high
mountains, high mountains, medium-high mountains, low mountains, hills
and plains. The region also features glacier edge, karst, sandstorm
and volcanic topographies.
Mountains
Some 20 million years ago, the Asian, European and Indian Ocean continental
plates collided, resulting in the elevation of the world's youngest
plateau--the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Mountains created as a result
form the skeleton of Tibet.
Mountains Running From East to West
Kunlun Mountains: Kunlun runs from west to east on
the northern fringe of the Tibetan Plateau. To its north is the Tarim
Basin in Xinjiang and the Qaidam Basin in Qinghai; to its south is
low-lying land, lake basins and wide valleys. Mostag, rising 6,973
meters above sea level, is the highest peak in the area.
Kalakunlun-Tanggula Mountains: The major part
of the Kalakunlun Mountains lies on the border between Xinjiang and
Kashmir. Running eastward, it forms the Tanggula Mountains at 90°E,
marking the border between Tibet and Qinghai.
Kangdese-Nyainqentanglha Mountains: Tucked away
at the southern edge of the North Tibet Plateau, the mountains serve
as the border between south and southeast Tibet, and the demarcation
line for rivers that flow inside and outside the region. Kangrinboqe,
with an elevation of 6,656 meters, is the highest peak of the Kangdese
Mountains; and Nyainqentanglha, with an elevation of 7,162 meters,
is the highest peak of the Nyainqentanglha Mountains.
Himalayan Mountains: Zigzagging through the southern
part of the Tibetan Plateau, the Himalayas comprise almost parallel
mountains running from east to west. The major part of the Himalayas
lies on the border between China and India, and between China and
Nepal. Extending some 2,400 km, it is 200-300 km wide, and has an
average elevation of over 6,000 meters. In this part of the world
there are 80-odd peaks each with an elevation of over 7,000 meters,
and over 10 with an elevation over 8,000 meters. Qomolangmo, rising
8,848.13 meters above sea level, towers over surrounding peaks in
the middle part of the Himalayas on the Sino-Nepalese border. Within
an area of 5,000-plus square km surrounding the world's highest are
four more peaks each with an elevation of over 8,000 meters and 38
rising over 7,000 meters.
Mountains Running From South to North
Hengduan Mountains: Hengduan is a combination
of several parallel mountains, including Bexoi La and Mangkam Mountains.
Rivers
In the Tibet Autonomous Region there are some 20 rivers each with
a drainage area of over 10,000 square km, and over 100 rivers with
a drainage area of over 2,000 square km. The most important are the
Jinshajiang, Nujiang, Lancangjiang and Yarlung Zangbo. The region
is the source of some of the most famous rivers in Asia, such as the
Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra, Mekong, Salween and Irrawaddy.
Yarlung Zangbo is the largest river in the autonomous region. Originating
in the Gyima Yangzong Glacier in Zhongba County at the northern foot
of the Himalayas, it runs 2,057 km in China (ranking fifth in China
in terms of length), draining an area of 240,480 square km (sixth
in China). With the drainage area 4,500 meters above sea level, the
Yarlung Zangbo is the highest river in the world. When it flows into
India via Lhoyu, it is called the Brahmaputra River.
About 1 million people, or half of the population in the autonomous
region, live in the area drained by the Yarlung Zangbo River with
153,333 hectares of cultivated land, or 50 percent of the Tibetan
total. The area is also home to some major cities and towns, including
Lhasa, Xigaze, Gyangze, Zetang, and Bayi.
The Yarlung Zangbo River turns to the northeast after Paiqu in Mainling,
and makes a U-turn around Namjagbarwa, the highest peak in the eastern
Himalayas to create the largest canyon in the world. The Yarlung Zangbo
Grand Canyon is 5,382 meters deep, the deepest in the world. The river
bottom is 74 meters at the narrowest part and 200 meters at the widest
part, extending 370 km in length.
Lakes
The Tibetan Plateau is dotted with some 1,500 lakes, including Nam
Co, Serlin Co and Zhari Nam Co, each with an area of over 1,000 square
km, 47 covering more than 100 square km each and 612 others covering
more than 1 square km each. Lake areas add up to 24,183 square km,
or one-third of the total in China. Seventeen lakes are tucked away
at an elevation of 5,000 meters or higher; each covering an area of
over 50 square km.
Climate
Overall, the Tibetan climate features frigid and dry air in the northwest
and warm and humid in the southeast, forming overlapping climatic
zones, such as the subtropical/warm, temperate/sub-frigid zones, and
the humid/semi-humid and semi-dry/dry zones. In response to the varied
climatic zones, Tibet is divided into different areas in terms of
plants: forests, bush, grassy marshland, grassland and desert.
 Generally
speaking, Tibet is blessed with varied forms of climatic zones, which
combine to make the autonomous region a land with much more sunshine,
stronger radiation, greater difference in temperature between day
and night, a clear distinction between dry and wet days, and plentiful
night rainfall. Winter and spring are dry and windy, with low atmospheric
pressure and relatively low oxygen content in the air. As the region
enjoys much more sunshine than many parts of the world and stronger
radiation, winter is comparatively warm during the day; the temperature
dropping below zero only at night. Generally
speaking, Tibet is blessed with varied forms of climatic zones, which
combine to make the autonomous region a land with much more sunshine,
stronger radiation, greater difference in temperature between day
and night, a clear distinction between dry and wet days, and plentiful
night rainfall. Winter and spring are dry and windy, with low atmospheric
pressure and relatively low oxygen content in the air. As the region
enjoys much more sunshine than many parts of the world and stronger
radiation, winter is comparatively warm during the day; the temperature
dropping below zero only at night.
In Tibet, each cubic meter of air contains only 62-65.4 percent of
oxygen in the air on the plains.
Tibet boasts more solar radiation than any other part of China, amounting
to 100 percent, one-third more than in plains at the same latitude.
In addition, Tibet enjoys longer daily sunshine, reaching 3,021 hours
annually in Lhasa. However, it is 1,186.84 hours in Chengdu and 1,932.5
hours in Shanghai. The difference in atmospheric temperature between
day and night is enormous in Tibet; however, so far as the whole year
is concerned, the seasonal difference is small. The atmospheric temperature
in a year, and during the hottest days in Lhasa and Xigaze, stays
10-15°C lower than in Chongqing, Wuhan and Shanghai. The seasonal
difference in atmospheric temperature in Lhasa, Qamdo and Xigaze reaches
18-20°C. In the Ngari area, 5,000 meters above sea level, the
atmospheric temperature in August reaches over 10°C or higher
during the day, but falls to below zero at night.
Precipitation is unevenly distributed in various localities in Tibet,
with a remarkable demarcation line between dry and rainy seasons.
It rains frequently at night. Annual precipitation amounts to 5,000
mm in the low-lying area in the southeastern part, dropping to 50
mm in the northwest. Precipitation in the period from October to April
makes up only 10-20 percent of the annual total, while precipitation
in the period from May to September accounts for the rest.
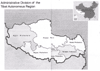
Administrative Division
The Tibet Autonomous Region exercises jurisdiction over one city and
six prefectures, with one district under the city government, one
county-level city, 71 counties, one county-level port and one county-level
special administrative area.
Lhasa is the capital and the region's political, economic, cultural
and transport center. A cultural city with a history of over 1,300
years, Lhasa sits on the northern bank of the Lhasa River, a tributary
of the Yarlung Zangbo River. With an elevation of 3,658 meters, the
city covers an area of close to 30,000 square km , including a downtown
area of 544 square km.
It has a population of 403,700 people, including 140,000 living in
the downtown area. They are of the Tibetan, Han, Hui and some other
ethnic groups, with people of the Tibetan ethnic group making up 87
percent of the total.
|
|

