In China, there is a large working-age population, while the average educational level of the people is relatively low, resulting in a very prominent problem of unemployment. This is primarily manifested in the co-existence of the contradiction of the total volume of workforce supply and demand and the contradiction of employment structure, in the simultaneous appearance of increasing pressure on urban employment and acceleration of the shift of surplus rural laborers to non-agricultural sectors, and in the intertwining of the employment problem for new entrants to the workforce and that of the reemployment for laid-off workers.
Population and workforce
In 2003, the total population of China reached 1.292 billion (excluding Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region and Taiwan Province). The population over the age of 16 was 998.89 million, of which the urban population was 423.75 million and the rural population 575.14 million; the economically active population was 760.75 million and the workforce participation rate was 76.2 percent. Among the population over the age of 16, the population with junior middle school education level and above took up 61.7 percent, and that with junior college education level and above, 6.6 percent. Among the population of technical workers, those of the elementary grade took up 61.5 percent, those of the intermediate grade, 35 percent, and those of the advanced grade, 3.5 percent.
Total employment
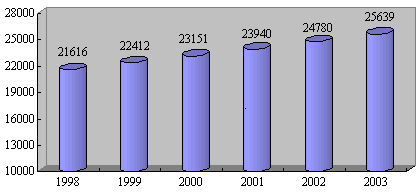
In 2003, the total urban and rural employed population reached 744.32 million (see Chart 1), of which the urban employed population was 256.39 million, accounting for 34.4 percent (see Chart 2), and the rural employed population was 487.93 million, accounting for 65.6 percent. From 1990 to 2003, the employed population increased by 96.83 million, an average increase of 7.45 million per annum.
Chart 1. Changes in the number of employees in urban and rural areas
(Unit: 10,000 people)
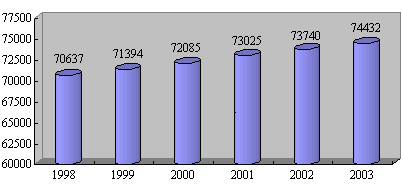 |
Chart 2. Changes in the number of employees in urban areas
(Unit: 10,000 people)
 |
Employment structure
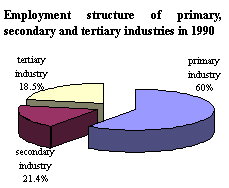
As far as the employment structure is concerned, from 1990 to 2003 the proportion of those employed in tertiary industry rose steadily from 18.5 percent to 29.3 percent, with the number of employees reaching 218.09 million; the proportion of those employed in secondary industry remained at around 21.6 percent, with the number of employees reaching 160.77 million; and the proportion of those employed in primary industry dropped from 60.1 percent to 49.1 percent, with the employees numbering 365.46 million (see Chart 3).
Chart 3.
 |
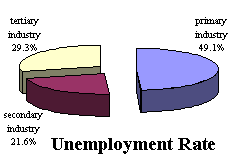 |
In terms of employment structure by urban and rural areas, from 1990 to 2003, the ratio of the employed in rural areas dropped from 73.7 percent to 65.6 percent. In terms of employment structure by different economic sectors, from 1990 to 2003, the number of employees in state-owned entities decreased by 34.7 million, down to 68.76 million; the number of those employed by urban individual and private economic entities increased by 35.96 million, to reach 42.67 million, representing 46.5 percent of the newly employed in the urban areas in the same period.
New forms of employment mushroomed, such as jobs in foreign-invested firms and economic entities of diverse forms, part-time jobs, temporary jobs, seasonal jobs, work on an hourly basis and jobs with flexible working hours, and became important avenues for the expansion of employment.
Unemployment rate
In recent years, as the employment pressure has been continuously increasing, the Chinese government has adopted many measures to curb the sharp rise of urban unemployment. By the end of 2003, the registered unemployment rate in the urban areas was 4.3 percent, and the number of registered jobless urbanites was eight million (see Chart 4).
Chart 4. Registered urban unemployment rate, 1990-2003 (%)
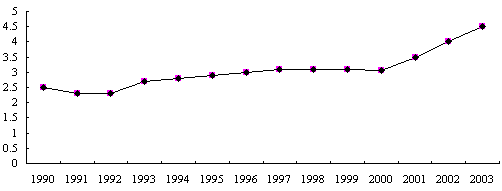 |
In 2004, the Chinese government has plans to find employment or reemployment for nine million people, and reemployment for five million laid-off persons, of whom the number of those who have difficulties finding a new job is one million. The registered unemployment rate in the urban areas is planned to be controlled at around 4.7 percent.
Income of urban and rural residents
As the economy develops and job opportunities increase, the income of urban and rural residents keeps rising. From 1990 to 2003, the disposable income per capita of urban residents rose from 1,510 yuan to 8,472 yuan, an increase of 460 percent or a rise of 160 percent in real terms; and the net income per capita of rural residents increased from 686 yuan to 2,622 yuan, an increase of 280 percent, or a rise of 77 percent in real terms (see Chart 5).
Chart 5. Income of urban and rural residents, 1990-2003
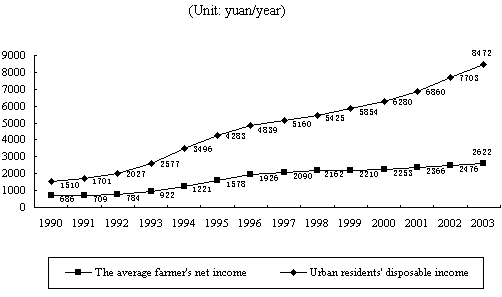 |